With the increasing advancement of car technologies around the world there has been an increasing demand of a large number of private cars. Moreover the busy schedule and high paying jobs of the humans open allows them to buy personal vehicles. Owning a private vehicle is now necessity rather than being a luxury, as it was during the earlier days. ...
Read More »Search Results for: scientists
A Look at the Technological Changes That are Reshaping the Medical Science Industry
It’s apparent from even a cursory scan of the trade journals or the science pages of a newspaper that we are living through a golden age for medical technology. Advances are coming through thick and fast, with breakthroughs around the corner that could have a decisive impact on global health and life expectancy. Of course there will be challenges to ...
Read More »5 Sci Fi Movie Gadgets That Exist in Real Life
Sci-fi movies have long promised an eventful future filled with spaceships and worker robots. Surprisingly enough, not everything from sci-fi movies is fantasy. Sure, we don’t have anti-gravity landspeeders yet, but check out this list for swanky gizmos from sci-fi movies that have already become a reality: 1. Robots Who doesn’t love R2D2, C3PO and Wall-E? The number of sci-fi ...
Read More »New Technology Inspired by Nature
Nature and technology have historically been in conflict with one another. The traditional view of technology is to create unnatural things that empower people to do things that would not be possible through naturally occurring forces. However, the emergence of generative design is re-shaping how designers and inventors view the relationships between nature and technology. Through the use of generative ...
Read More »Focus@Will Review
Music plays a role in the lives of nearly every person alive on this earth. Grant it, everyone has different tastes and enjoys listening to various genres, as well as artists. Whether it is the radio while traveling in the car to and from work, soothing dinner music or some tunes to either relax with or rock out with; there ...
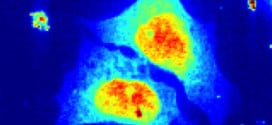
Read More »Take A Look At The First Ever Living Cell X-Ray!
Take a look at the first living cell x-ray pictured below. A new technique developed enabled scientists to view this cell without killing it or changing its composition.
Read More »The Lakemaid Beer Delivery Drone Is No More!
While fishermen on Lake Waconia in Minnesota were thrilled with the Lakemaid beer delivery drone, it seems that the FAA was not so much.
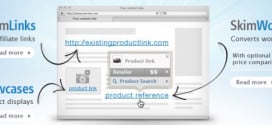
Read More »$500M+ In E-Commerce Sales For Skimlinks Last Year!
Skimlinks, known for their affiliate marketing services had a record year last year driving over $500 million in e-commerce sales to online publishers through affiliate links!
Read More »Silkworms Produce Dyed Silk After Eating Dyed Mulberry Leaves
We're not exactly sure whether it's a a good thing to feed silkworms dyed food but someone thought so and when they did something pretty cool happened...
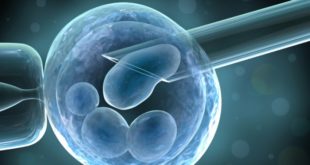
Read More »Grown Human Heart Tissue That Can Beat!
A team of researchers at the University of Pittsburgh have accomplished the incredible and grown human heart tissue that can beat autonomously. The tissue was created using pluripotent stem cells that came from mature human skin.
Read More » Gearfuse Technology, Science, Culture & More
Gearfuse Technology, Science, Culture & More